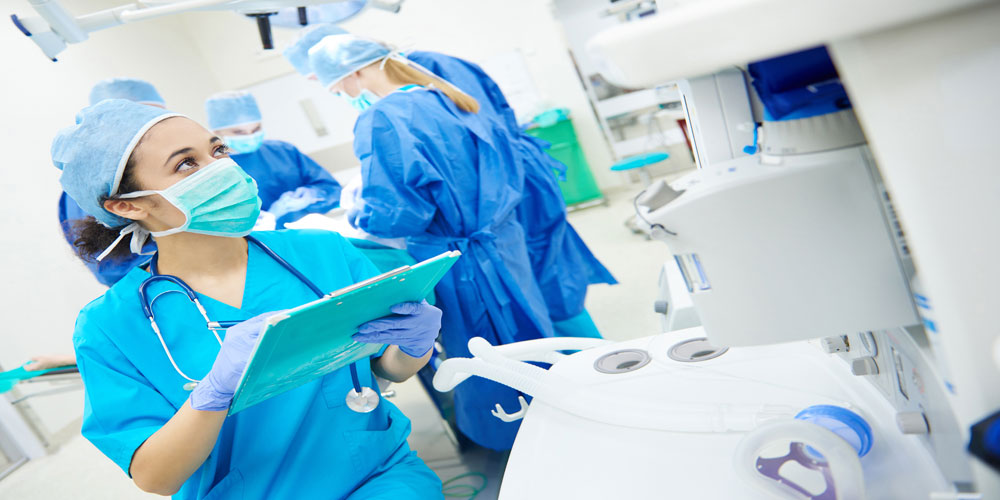
Barrier nursing is a type of infection control technique used in healthcare settings to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. This technique involves the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and strict isolation measures to reduce the risk of transmission of infectious agents between healthcare workers, patients, and visitors.
Barrier nursing presents several challenges for nurses:
One of the primary challenges associated with barrier nursing is the increased workload for nurses. Nurses must spend more time donning and doffing PPE, which can be time-consuming and physically demanding. Additionally, the use of PPE can make it difficult for nurses to communicate with patients, as the use of masks and face shields can make it harder to hear and understand patients. This can lead to miscommunication and frustration for both the nurse and the patient.
Another challenge is the psychological impact of barrier nursing on nurses. The isolation measures used in barrier nursing can cause patients to feel lonely, anxious, and depressed. This can be particularly challenging for nurses who are responsible for caring for patients in isolation for extended periods. Nurses may experience feelings of guilt, frustration, and helplessness when they are unable to provide emotional support to patients due to isolation measures.
Barrier nursing can increase the risk of nurse burnout. Nurses may feel isolated and unsupported when they are working in isolation rooms or wearing PPE for extended periods. This can lead to feelings of exhaustion, emotional detachment, and depersonalisation. Nurses who work in barrier nursing may also experience a higher risk of contracting infectious diseases, which can lead to absenteeism and the need for replacement staff.
Some other issues to be considered include:
Physical discomfort: The prolonged use of PPE can cause physical discomfort and fatigue for nurses. Wearing masks and face shields can cause skin irritation and pressure sores, while gowns and gloves can be hot and restrictive, making it difficult for nurses to move and perform tasks.
Communication barriers: The use of PPE can also make it difficult for nurses to communicate with colleagues and other healthcare professionals. The muffling of sound and lack of visibility can make it hard to hear and understand instructions, leading to errors and misunderstandings.
Emotional distress: Barrier nursing can be emotionally distressing for nurses, especially when caring for patients with highly infectious diseases. The fear of contracting the disease, the isolation, and the uncertainty surrounding the disease’s outcome can cause significant stress and anxiety for nurses.
Social isolation: Nurses practicing barrier nursing are often isolated from their colleagues and other healthcare professionals. This can lead to feelings of loneliness and disconnection from the team, further exacerbating the emotional impact of the job.
Training and education: Nurses require adequate training and education to effectively practice barrier nursing. However, the lack of resources and time can make it challenging for healthcare organisations to provide the necessary training and education for their nurses.
Patient-centered care: Barrier nursing can make it difficult for nurses to provide patient-centered care. The use of PPE and isolation measures can create barriers between the nurse and the patient, making it difficult to establish trust and build a therapeutic relationship.
Finally, there are financial challenges associated with barrier nursing. The cost of PPE and other infection control measures can be high, and healthcare organisations may struggle to balance the need for effective infection control with the cost of providing PPE and isolation facilities. This can lead to resource shortages and inadequate staffing, which can further increase the workload and stress on nurses.
While barrier nursing is a necessary infection control technique, it presents several challenges for nurses. The increased workload, psychological impact, risk of burnout, and financial challenges associated with barrier nursing can have a significant impact on nurses and their ability to provide quality care to patients. Healthcare organisations must prioritise the well-being of nurses and provide them with the resources and support they need to perform their jobs effectively while minimising the risks associated with barrier nursing.